How a cloud-based SaaS platform like Site24x7 makes network monitoring easy
The importance of proactive event handling in modern IT observability
Events are actionable signals derived from observability's core pillars—metrics, traces, and logs—that are converged to deliver end-to-end visibility across your tech stack. They can be used to flag operational shifts or anomalies, such as server crashes, traffic surges, or sluggish database queries. Events from metrics highlight latency,...
Addressing configuration management in legacy network systems
Behind the screens: Site24x7’s Google Cloud Monitoring architecture
Monitoring your vast cloud environments is an important aspect of achieving such performance. Site24x7 Google Cloud Monitoring has been an indispensable tool for you and thousands of IT professionals to maintain the health and availability of Google Cloud resources.
Have you ever wanted to know how Site24x7 does it without breaking a sw...
The secret to a stable internet: Why monitoring WAN links is essential
Website monitoring checklist
Website monitoring can be much more effective with more specifics and details. Before diving into the specifics of monitoring, it's best to define your goals and preferences first. What is your target for implementing the monitoring? Is a better uptime all you are looking for, or do you wish to fine-tune your site's user experience?
Why network observability is a boardroom priority for CEOs
How to master the SGA and PGA in Oracle databases
As we are talking about Oracle databases here, you are probably aware of the system global area (SGA) and program global area (PGA) in Oracle, which play a crucial role in database memory management. Let us explore memory allocation in detail and how to configure these for peak efficiency.
The SGA and PGA in Oracle are critical for memo...
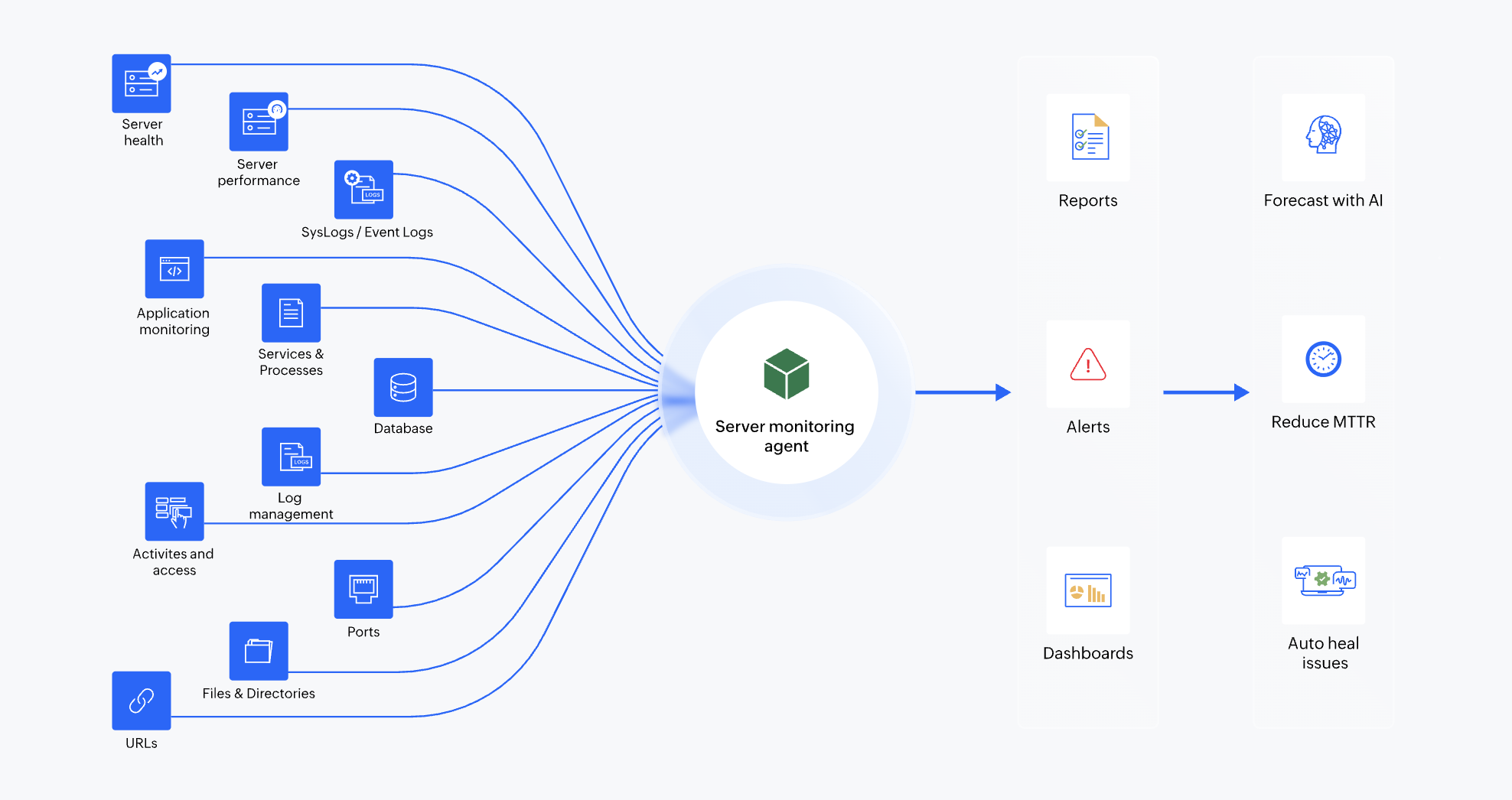
Maximizing ROI in server monitoring: A strategic approach for businesses
According to the 2024 Statista report on global crucial data center IT outages from 2020-2023 , power disruptions have become the leading cause of outages, rising from 37% in 2020 to 52% in 2023. This shift highlights an increasing vulnerability in infrastructure reliability, making proactive server monitoring more critical than ever. Want to...
Using eBPF for modern IT observability: challenges and opportunities
Today, eBPF is a powerful, widely accepted technology that operates at the kernel level of the operating system. It enables real-time, low-overhead monitoring of system calls, network traffic, and resource usage across applications and containerized deployments. Celebrated system performance expert and author Brendan Gregg once quipped that &...